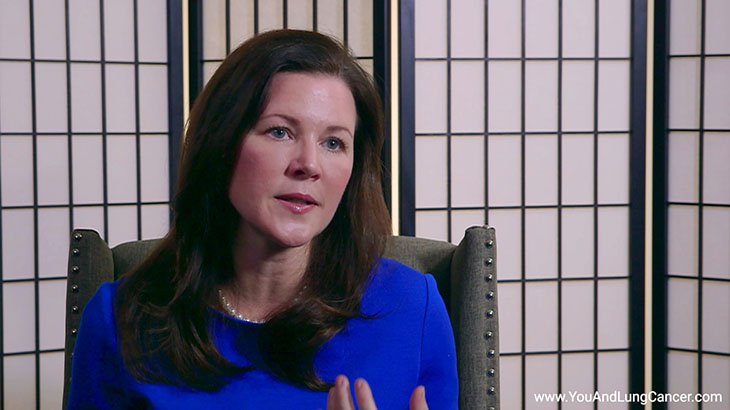
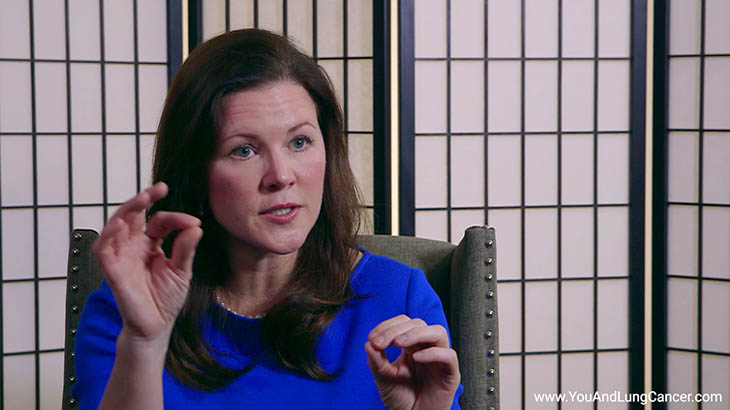
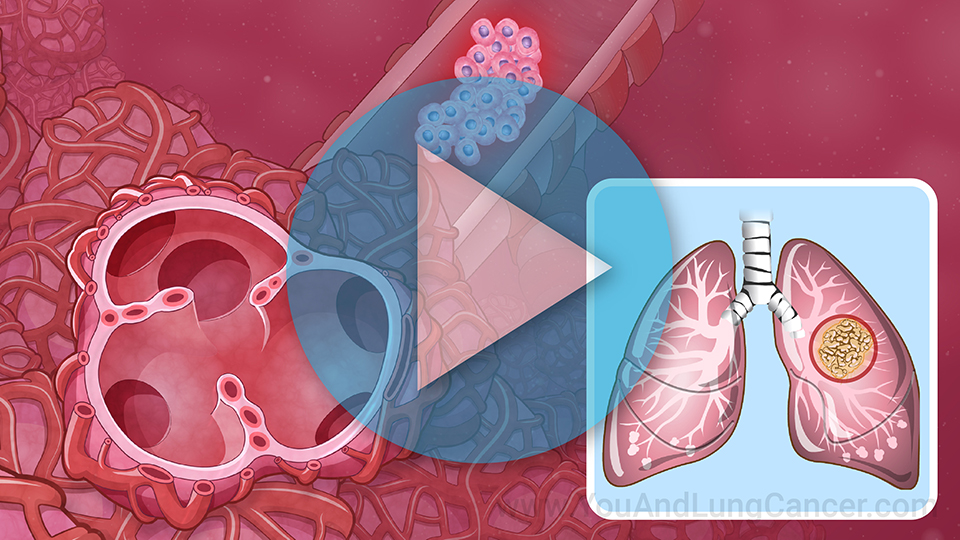
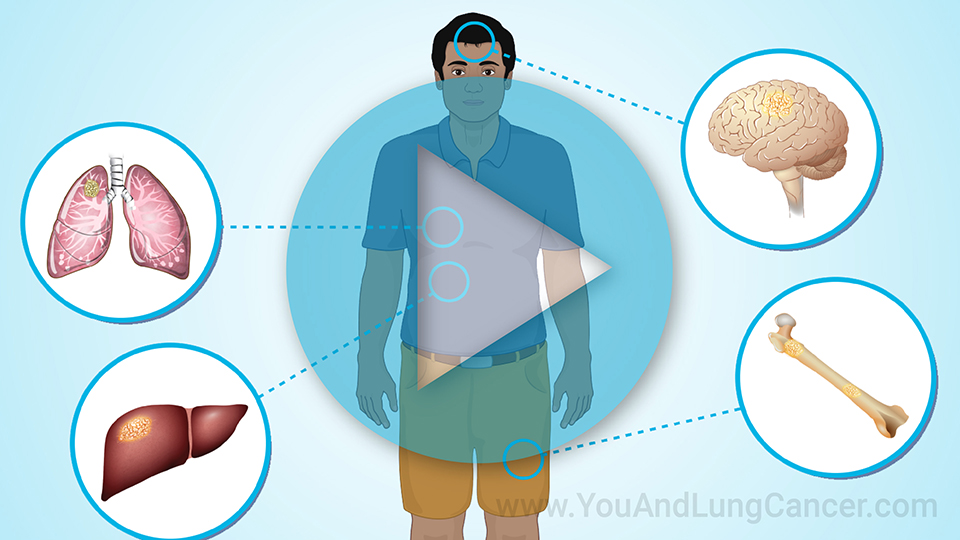
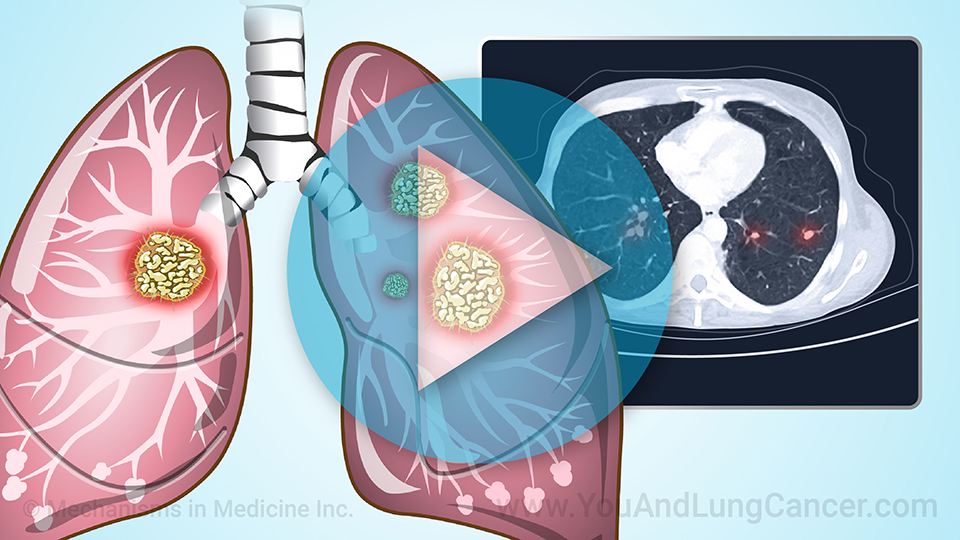
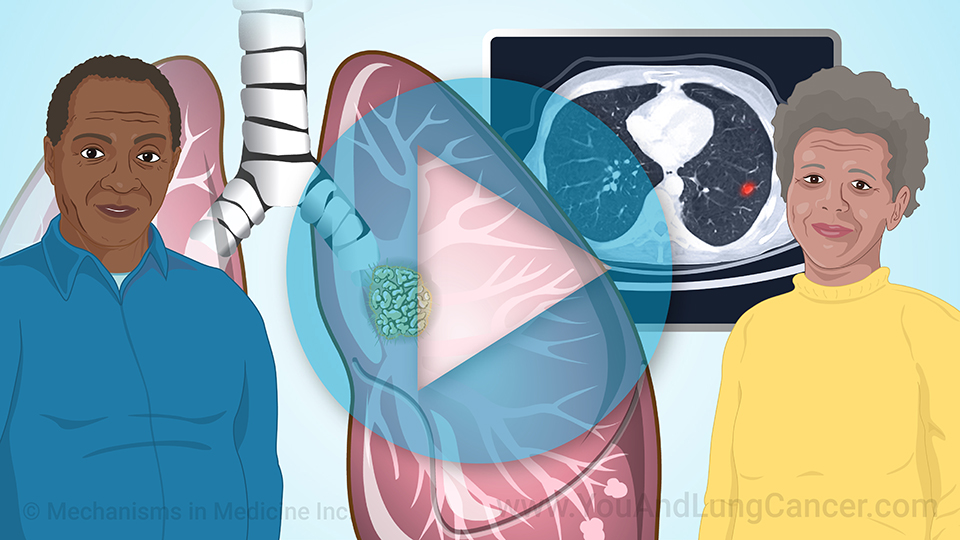
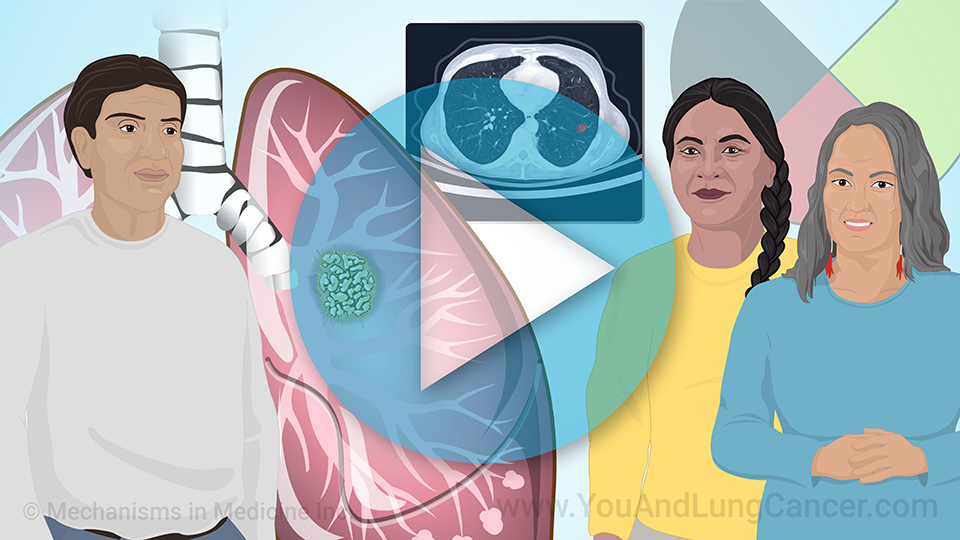
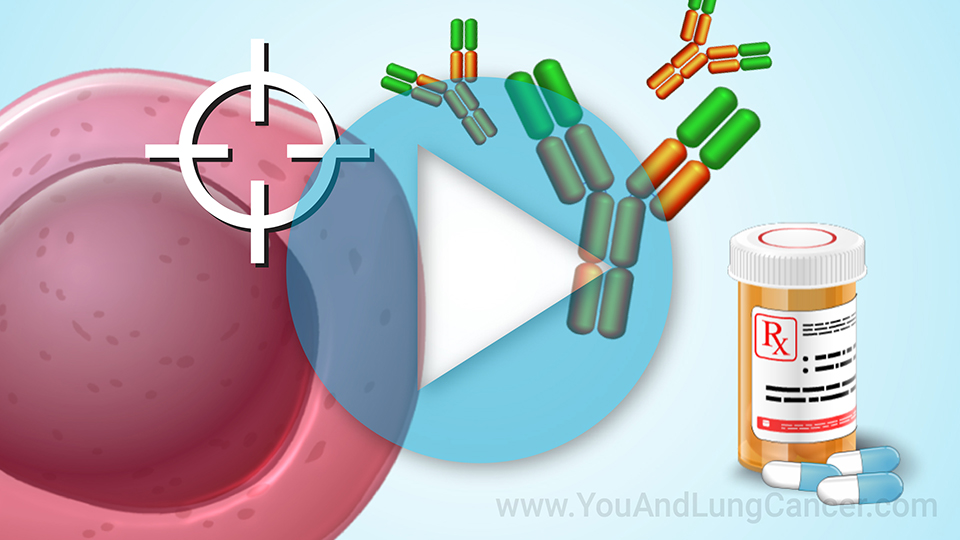
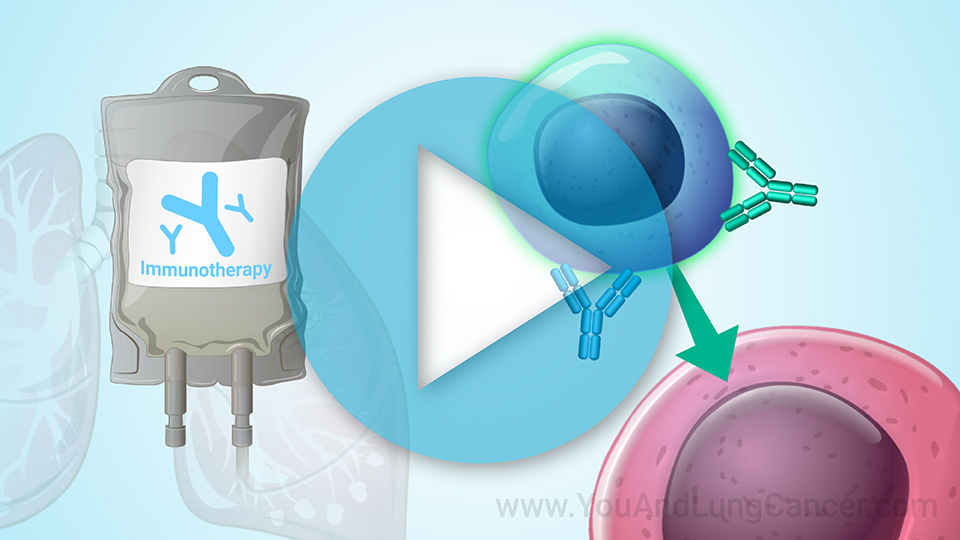
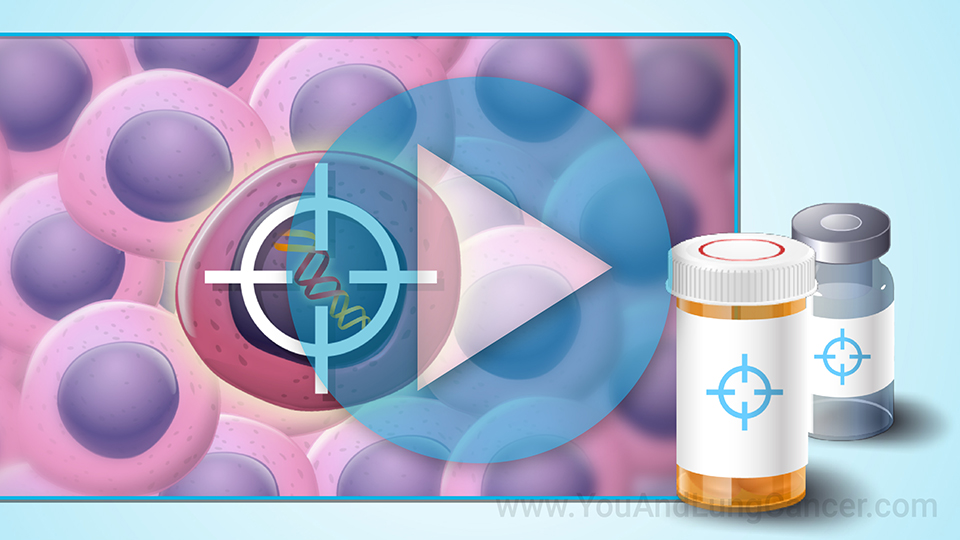
Diagnosis of non-small cell lung cancer is “tissue based”. This means that typically if a patient has been given a CAT Scan or X-Ray which identifies an abnormality in the lungs, the next step is to do a biopsy which can done in a variety of ways. It can be done by the radiologist at the time of the CAT scan (or CT scan). A piece of the tissue is looked at by a pathologist under the microscope. Another way is using a “bronchoscopy” which involves a tube being placed through the nose or into the mouth and into the airway. The pulmonologist can use this tool to see the cancer and then take a sample of the tissue for biopsy. In some cases, surgeons can be involved in the diagnosis of small cell lung cancer. In these cases its usually when the cancer is located in places like the lymph nodes which are difficult for the pulmonologist or radiologist to reach.
-
Share with family and friends:
Click here to take our SURVEY
Your feedback is important to us! We will use your feedback to develop future areas of content about lung cancer which will help other patients, caregivers and families.